Adapter Overview
An adapter is a “driver” program that enables Neuron ESB to interact with a new kind of endpoint, such as a legacy system, proprietary system, or line of business application.
Figure 1 illustrates why adapters are needed: you may encounter systems from time to time that Neuron does not know how to communicate with.
Figure 2 shows the role of an adapter. The adapter knows how to communicate natively with the target system and also how to communicate with Neuron. With the adapter in place, the ESB and the target system can interact.
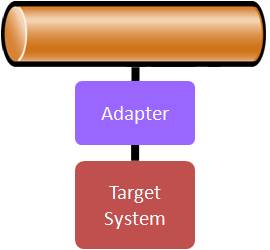
Neuron ESB adapters serve to abstract the Target System so that they can be managed and interacted with just like any existing service endpoint. Adapters can encapsulate proprietary or 3rd party API, Logic and/or Transports specific to communicating with the Target System. Using adapters enables developers to interact with other 3rd party systems in a much more standardized way, without having to know specifics about the target system.
Adapters can support a variety of communication patterns such as one way, two way, service provider or service consumer.
Metadata
Many Neuron .NET adapters support metadata. Metadata is additional information above and beyond the payload data passed between the ESB and an adapter. Examples of metadata include the following:
- For a file adapter, metadata includes path, file name, file type, length, creation time, and whether or not the file is read-only.
- For an MSMQ adapter, metadata includes message Id, label, correlation Id, priority, and source machine.
- For an EMail adapter, metadata includes To/Cc/From addresses, subject, message body, and attachment.
Metadata is stored in an ESB Message’s custom property area which contains name/value pairs. The name of properties that originate as metadata are prefixed to indicate which adapter they are associated with, and optionally whether they apply to inbound messages or outbound messages. For example, the file adapter’s property names for received files are all prefixed with “file_in.”.
The relationship between adapters, metadata, and ESB messages is as follows. Note this only occurs if an adapter endpoint definition has the Include Metadata check box checked.
- Publishing. When an adapter has new data to pass to the bus, it fashions an ESB message. If Include Metadata has been enabled, information about the original data is added to the message’s custom properties area.
- Subscribing. When the bus passes information to an adapter to be sent to an endpoint, and Include Metadata has been enabled, the adapter scans for metadata properties in the ESB message which may alter how the information is delivered. For example, the file adapter allows an output file’s path, name, or type to set through the custom properties file_out.Path, file_out.Name, and file_out.Type.
The metadata properties are not always bi-directional; it is typical that on a receive there may be a large set of metadata properties but on a send only a handful of properties have significance at send time. The reason for this is that many of the receive-side properties are read-only.
See Also: Refer to the individual adapter documentation for details about the specific metadata properties supported.
Types of Adapters
Neuron .NET Adapters
Neuron .NET adapters ship with Neuron ESB. They are built using the Neuron Adapter Interfaces and API. All Neuron .NET adapters are installed and loaded from \Adapters folder located at the root of the Neuron ESB program installation directory. When writing custom adapters, they must be copied to the Adapters folder.
The following Neuron .NET Adapters can be installed during setup:
| Name | Description | Mode |
| File Adapter | Supports polling a folder and Folder change events for messages to publish. Supports writing messages to a folder. | Publish, Subscribe |
| FTP/FTPS Adapter | Supports polling an FTP site/folder and for messages to publish. Supports writing messages to an FTP site/folder. | Publish, Subscribe |
| MSMQ Adapter | Supports polling MSMQ for messages to publish. Supports writing message to a queue | Publish, Subscribe |
| SQL Adapter | Supports polling SQL Server for messages to publish. Supports inserts, deletes and request against SQL Server | Publish, Subscribe, Execute, Query |
| ODBC Adapter | Supports polling ODBC data sources for messages to publish. Supports inserts, deletes and request against ODBC data sources | Publish, Subscribe, Execute, Query |
| ActiveMQ Adapter | Supports polling an ActiveMQ for messages to publish. Supports writing message to a queue | Publish, Subscribe |
| BizTalk RFID Event Handler | Supports receiving events from a RFID reader | Publish |
| Email Adapter | Supports sending SMTP messages | Subscribe |
| CRM Subscription AdapterCRM Workflow AdapterCRM Plug-in Adapter | Supports sending messages to (Subscribe) and event based publication from Microsoft Dynamics CRM 4 and 2011 | Publish, Subscribe |
| eConnect Adapter | Supports communication to Microsoft Dynamics Great Plains | Subscribe, SubscribeTwoWay, Query |
| SharePoint Subscription AdapterSharePoint Publication Adapter | Supports sending messages to (Subscribe) and event based publication from Microsoft SharePoint Server | Publish, Subscribe |
| Websphere MQ Adapter | Supports polling an MQSeries for messages to publish. Supports writing message to a queue. Also supports both service consumer and provider patterns using MQSeries correlation across the bus. | Publish, Subscribe, SolicitResponse, RequestReply |
Neuron .NET Plug-ins
Neuron ESB also ships two special adapters that are event based, and hosted in the application in which they are the publisher for. These adapters are the SharePoint Publication Adapter and the CRM Workflow Adapter. The setup program for these can be found in the respective sub directory under the \Plugins folder located at the root of the Neuron ESB program installation directory.
WCF LOB Adapters
WCF LOB adapters are adapter programs written using the Microsoft WCF LOB SDK SP2. To use WCF LOB Adapters, the Microsoft LOB SDK SP2 MUST be downloaded and installed on the Neuron ESB Server and where ever the Neuron ESB Explorer will be used to configure the Adapter Endpoint.
By supporting the WCF LOB Adapter SDK SP2, the Microsoft BizTalk Adapter Pack 2.0 adapters may be used and configured as Adapter Endpoints within Neuron.
The Microsoft BizTalk Adapter Pack 2.0 provides the following adapters:
| Name | Description | Versions Supported |
| Microsoft BizTalk Adapter 3.0 for Siebel eBusiness Applications | This adapter enables clients to invoke Business Services and operations on Business Components in a Siebel eBusiness Application. | Siebel 7.5 (7.5.3.15)Siebel 7.7 (7.7.2.8)Siebel 7.8 (7.8.2.6)Siebel 8.0 (8.0.0.1) |
| Microsoft BizTalk Adapter 3.0 for mySAP Business Suite | This adapter enables clients to exchange Intermediate Document (IDOC), BAPI, and Remote Function Call (RFC) messages with the SAP system. | SAP R/3 4.6c Non-UnicodeSAP R/3 4.7 Non-UnicodeSAP R/3 4.7 UnicodeSAP R/3 5.0 Non-UnicodeSAP R/3 5.0 UnicodeSAP R/3 6.0 Unicode |
| Microsoft BizTalk Adapter for Oracle E-Business Suite | Using this adapter clients can perform operations on the the Oracle E-Business Suite artifacts (PL/SQL APIs, interface tables/views, concurrent programs, and request sets) and the underlying Oracle database artifacts (such as tables, functions, and procedures) by exchanging SOAP messages with the adapter. | The Oracle E-Business adapter uses the Oracle Data Provider for .NET (ODP.NET) 11.1.0.7 to communicate with Oracle E-Business Suite. ODP.NET 11.1.0.7 is one of the components of Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC). |
| Microsoft BizTalk Adapter 3.0 for Oracle Database | This Oracle database adapter enables adapter clients to read and write to and Oracle database | Oracle 9.2Oracle 10.1Oracle 10.2Oracle 11.1The Oracle Database adapter supports Oracle Data Access Components for Oracle Client 11.1.0.6 with Patch Set 11.1.0.7. |
| Microsoft BizTalk Adapter for SQL Server | The Microsoft BizTalk Adapter for SQL Server exposes the SQL Server database as a WCF service. Adapter clients can perform operations on the SQL Server database artifacts such as tables, views, and procedures by exchanging SOAP messages with the adapter | SQL Server 2000SQL Server 2005SQL Server 2008 |